Abstract:
Researchers from Kanazawa University have chemically modified Kraft lignin—ordinarily considered in the paper industry to be a waste product—and used it to produce quality carbon fiber. When optimized in the future as an automotive structural material, it may reduce the fuel needed to power your car.
Kanazawa, Japan – Given concerns over global climate warming, researchers are hard at work on minimizing the amount of fuel that we all use in everyday life. Reducing the weight of vehicles will lessen the amount of fuel required to power them, and put money back into your pocket.
In a study recently published in Chemical Engineering Journal, researchers from Kanazawa University have chemically modified an industrial waste product, and processed it into a possible lightweight structural material. This development may increase the fuel economy of private and commercial transportation.
The researchers started with Kraft lignin, a byproduct of a common wood pulping process. Paper mills usually burn Kraft lignin to generate power, because it's difficult to use for anything except specialized purposes. Chemically processing Kraft lignin into a more useful material would improve the environmental sustainability of paper production.
"We performed a chemical modification of Kraft lignin polymer known as acetylation," says first author László Szabó. "Optimizing the extent of acetylation was critical to our research effort."
A controlled reaction was important for optimizing Kraft lignin's ability to be compatible with another polymer called polyacrylonitrile, and thus prepare quality carbon fibers creating an engineered composite. If there's too little—or too much—acetylation, the carbon fibers are of low quality.
"Our reaction was quite mild, producing only a rather benign side product—acetone—without changing the polydispersity of the Kraft lignin," explains Kenji Takahashi, co-senior author. "We thus were able to mix Kraft lignin with polyacrylonitrile to obtain a dope solution for electrospinning containing more compatible polymer segments and eventually fabricate quality carbon fibers."
The researchers' carbon fiber mats contain fine uniform fibers, without the thermal treatment lessening fiber quality. In fact, compared with unmodified Kraft lignin, by using the modified polymer the fiber mat exhibited an almost 3-fold improvement in mechanical strength.
"Our fibers' mechanical performance is attributable to the tailored graphitic structure of the materials," explains Szabó. "This outcome is owing to the improved polymer interactions leading to a more aligned polymeric network which is then subjected to the thermal treatment."
Engineered composites are common in spacecraft, cars, plastic, concrete, and many other products and technologies. When these researchers minimize the cost of preparing their new carbon fibers, perhaps vehicles of the future will be lighter, more durable, and more fuel-efficient. Given that every industry uses transportation, everyone will save money and every business will be more environmentally sustainable.
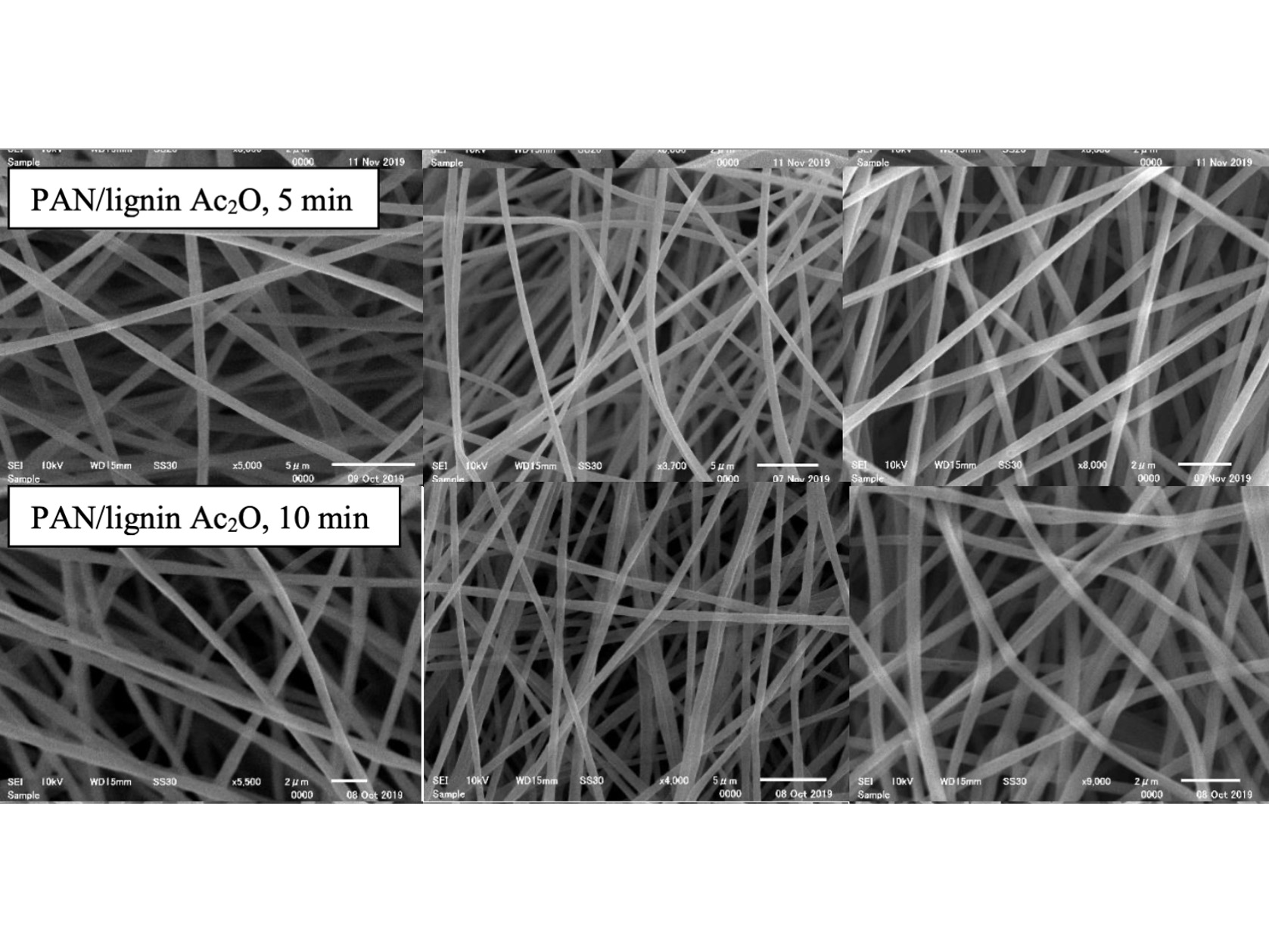
Figure 1
Fine carbon fiber network fabricated using optimized conditions (from left to right: electrospun fibers, thermally stabilized fibers, carbon fibers).
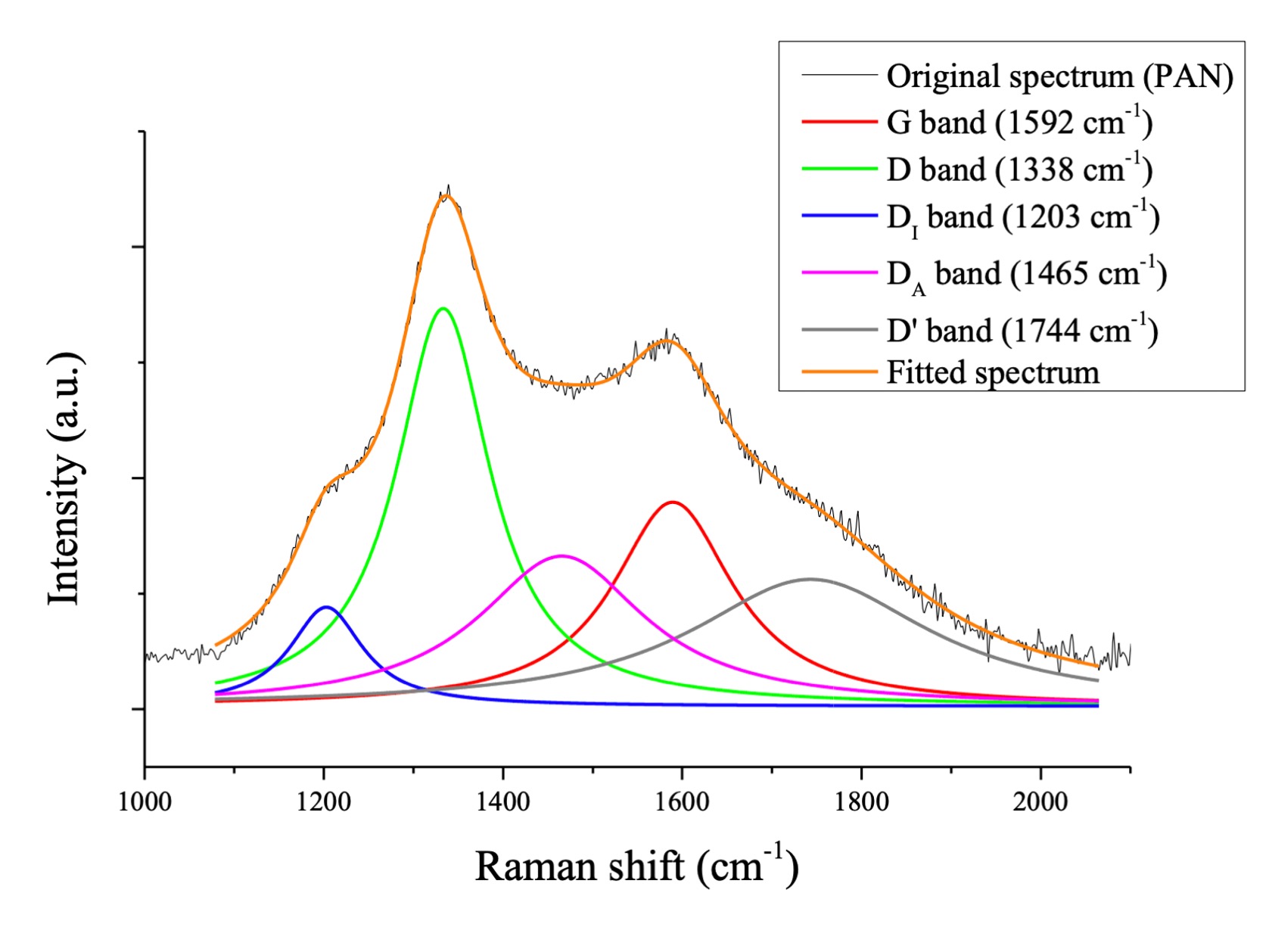
Figure 2
Typical Raman spectrum recorded on a carbon fiber mat showing contributions from graphitic and defect derived peaks.
Article
Controlled acetylation of kraft lignin for tailoring polyacrylonitrie-kraft lignin interactions towards the production of quality carbon nanofibers
Journal: Chemical Engineering Journal
Authors: László Szabó, Romain Milotskyi, Hisai Ueda, Takayuki Tsukegi, Naoki Wada, Kenji Takahashi
DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.126640
Funder
The authors gratefully thank the financial support received through the Center of Innovation Science and Technology based Radical Innovation and Entrepreneurship Program (COI stream, (JPMJCE1315)) aimed at the “Construction of next generation infra- structure using innovative materials: Realization of a safe and secure society that can coexist with the Earth for centuries”, supported by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) and the Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST).



 PAGE TOP
PAGE TOP